For an overview of blockchain in financial services , visit this page: Blockchain in financial services. We examine some of the ways FS firms are using blockchain, and how we expect the blockchain technology to develop in the future. Explore how others might try to disrupt your business with blockchain technology, and how your company could use it to leap ahead instead.
Realtime Bitcoin Globe
Blockchain announcements continue to occur, although they are less frequent and happen with less fanfare than they did a few years ago. Still, blockchain technology has the potential to result in a radically different competitive future for the financial services industry. Contact us to learn more about what PwC Financial Services can do for you. Any blockchain solution, no matter how prescient, is only as good as its execution. This is where PwC excels—by offering proven expertise in managing complex implementation programs from start to finish.
Learn more. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network. Similarly, Bitcoin consists of thousands of computers, but each computer or group of computers that hold its blockchain is in a different geographic location and they are all operated by separate individuals or groups of people. However, private, centralized blockchains, where the computers that make up its network are owned and operated by a single entity, do exist.
In a blockchain, each node has a full record of the data that has been stored on the blockchain since its inception.
- What Happens to Bitcoin After All 21 Million Are Mined?;
- quest ce que bitcoin core?
- convert btc to brl.
- Bitcoin (BTC) statistics - Price, Blocks Count, Difficulty, Hashrate, Value.
- NEW BLOCK DETECTED.
- how long to mine a bitcoin;
- Bitcoin scalability problem;
For Bitcoin, the data is the entire history of all Bitcoin transactions. If one node has an error in its data it can use the thousands of other nodes as a reference point to correct itself.
- bitcointalk hodl post.
- Block (Bitcoin Block).
- Bitcoin scalability problem - Wikipedia.
- fast btc mining free.
- toko my style btc?
- quy doi btc ra vnd;
- Recent Blocks;
This way, no one node within the network can alter information held within it. This system helps to establish an exact and transparent order of events. This ensures that whatever changes do occur are in the best interests of the majority. Each node has its own copy of the chain that gets updated as fresh blocks are confirmed and added.
This means that if you wanted to, you could track Bitcoin wherever it goes. For example, exchanges have been hacked in the past where those who held Bitcoin on the exchange lost everything. While the hacker may be entirely anonymous, the Bitcoins that they extracted are easily traceable. If the Bitcoins that were stolen in some of these hacks were to be moved or spent somewhere, it would be known. Blockchain technology accounts for the issues of security and trust in several ways. First, new blocks are always stored linearly and chronologically.
After a block has been added to the end of the blockchain, it is very difficult to go back and alter the contents of the block unless the majority reached a consensus to do so. Hash codes are created by a math function that turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters.
- bitcoin pen drive.
- best wallet for mining bitcoin?
- abby martin bitcoin.
- 1 bitcoin gewinnen.
- Block - Bitcoin Wiki;
- Coin Dance | Bitcoin Block Details!
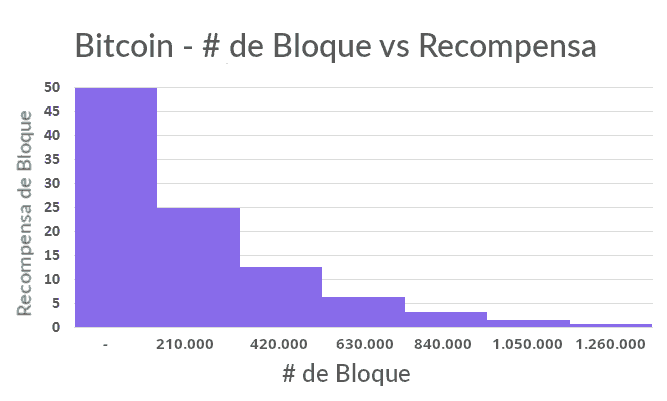
- Bitcoin in – Halving the Block Reward | Bitcoin Suisse;
If that information is edited in any way, the hash code changes as well. If they were to alter their own single copy, it would no longer align with everyone else's copy.
Bitcoin in 2021 – Halving the Block Reward
When everyone else cross-references their copies against each other, they would see this one copy stand out and that hacker's version of the chain would be cast away as illegitimate. Such an attack would also require an immense amount of money and resources as they would need to redo all of the blocks because they would now have different timestamps and hash codes. Not only would this be extremely expensive, but it would also likely be fruitless. Doing such a thing would not go unnoticed, as network members would see such drastic alterations to the blockchain.
The network members would then fork off to a new version of the chain that has not been affected. This would cause the attacked version of Bitcoin to plummet in value, making the attack ultimately pointless as the bad actor has control of a worthless asset. The same would occur if the bad actor were to attack the new fork of Bitcoin. It is built this way so that taking part in the network is far more economically incentivized than attacking it. The goal of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited.
Blockchain technology was first outlined in by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two researchers who wanted to implement a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with. The Bitcoin protocol is built on a blockchain. The key thing to understand here is that Bitcoin merely uses blockchain as a means to transparently record a ledger of payments, but blockchain can, in theory, be used to immutably record any number of data points. As discussed above, this could be in the form of transactions, votes in an election, product inventories, state identifications, deeds to homes, and much more.
Currently, there is a vast variety of blockchain-based projects looking to implement blockchain in ways to help society other than just recording transactions. One good example is that of blockchain being used as a way to vote in democratic elections.
Why was this done?
For example, a voting system could work such that each citizen of a country would be issued a single cryptocurrency or token. Each candidate would then be given a specific wallet address, and the voters would send their token or crypto to whichever candidate's address they wish to vote for. The transparent and traceable nature of blockchain would eliminate the need for human vote counting as well as the ability of bad actors to tamper with physical ballots.
Banks and decentralized blockchains are vastly different.
Block hashing algorithm
But it turns out that blockchain is actually a reliable way of storing data about other types of transactions, as well. Why do this? The food industry has seen countless outbreaks of e Coli, salmonella, listeria, as well as hazardous materials being accidentally introduced to foods. In the past, it has taken weeks to find the source of these outbreaks or the cause of sickness from what people are eating. If a food is found to be contaminated then it can be traced all the way back through each stop to its origin.
Not only that, but these companies can also now see everything else it may have come in contact with, allowing the identification of the problem to occur far sooner, potentially saving lives. This is one example of blockchains in practice, but there are many other forms of blockchain implementation. Perhaps no industry stands to benefit from integrating blockchain into its business operations more than banking.
Financial institutions only operate during business hours, five days a week. That means if you try to deposit a check on Friday at 6 p. Even if you do make your deposit during business hours, the transaction can still take one to three days to verify due to the sheer volume of transactions that banks need to settle. Blockchain, on the other hand, never sleeps.
With blockchain, banks also have the opportunity to exchange funds between institutions more quickly and securely. In the stock trading business, for example, the settlement and clearing process can take up to three days or longer, if trading internationally , meaning that the money and shares are frozen for that period of time. Given the size of the sums involved, even the few days that the money is in transit can carry significant costs and risks for banks. Blockchain forms the bedrock for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
The U. In , some of the banks that ran out of money were bailed out partially using taxpayer money. These are the worries out of which Bitcoin was first conceived and developed. By spreading its operations across a network of computers, blockchain allows Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to operate without the need for a central authority. This not only reduces risk but also eliminates many of the processing and transaction fees. It can also give those in countries with unstable currencies or financial infrastructures a more stable currency with more applications and a wider network of individuals and institutions they can do business with, both domestically and internationally.
Using cryptocurrency wallets for savings accounts or as a means of payment is especially profound for those who have no state identification. Some countries may be war-torn or have governments that lack any real infrastructure to provide identification. Citizens of such countries may not have access to savings or brokerage accounts and therefore, no way to safely store wealth. When a medical record is generated and signed, it can be written into the blockchain, which provides patients with the proof and confidence that the record cannot be changed.
These personal health records could be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key, so that they are only accessible by certain individuals, thereby ensuring privacy. In the case of a property dispute, claims to the property must be reconciled with the public index. This process is not just costly and time-consuming—it is also riddled with human error, where each inaccuracy makes tracking property ownership less efficient.
Blockchain has the potential to eliminate the need for scanning documents and tracking down physical files in a local recording office. If property ownership is stored and verified on the blockchain, owners can trust that their deed is accurate and permanently recorded. If a group of people living in such an area is able to leverage blockchain, transparent and clear timelines of property ownership could be established.
A smart contract is a computer code that can be built into the blockchain to facilitate, verify, or negotiate a contract agreement. Smart contracts operate under a set of conditions that users agree to. When those conditions are met, the terms of the agreement are automatically carried out. Say, for example, a potential tenant would like to lease an apartment using a smart contract. The landlord agrees to give the tenant the door code to the apartment as soon as the tenant pays the security deposit.
Both the tenant and the landlord would send their respective portions of the deal to the smart contract, which would hold onto and automatically exchange the door code for the security deposit on the date the lease begins. This would eliminate the fees and processes typically associated with the use of a notary, third-party mediator, or attornies. As in the IBM Food Trust example, suppliers can use blockchain to record the origins of materials that they have purchased. As reported by Forbes, the food industry is increasingly adopting the use of blockchain to track the path and safety of food throughout the farm-to-user journey.
Daily Bitcoin Mining Difficulty. Blocks Mined by Bitcoin Client. Blocks signaling more than one implementation are only counted once in the chart above. Blocks Mined by Bitcoin Client Compatibility historical.
Blocks signaling more than one implementation are counted multiple times in the above chart.